There are plenty of plagiarism checkers out there, both paid and free. However, if you are already using Microsoft Word for writing, you can use the built-in Similarity checker to quickly identify similar content online.
How to Use the Plagiarism Checker in Microsoft Editor on Word
Microsoft Editor is a grammar and spelling checker that’s free to use with Word Online. If you have a Microsoft 365 subscription, the desktop version of Word includes additional features, like the similarity checker, which helps you identify original content and add citations.
To use Similarity checker, open Word desktop or online, then click Editor in the Home tab. In the Editor pane (on the right side of your screen), go to Similarity and click Check for similarity to online sources. The status will change to Checking for similarity and may take a few minutes to complete.
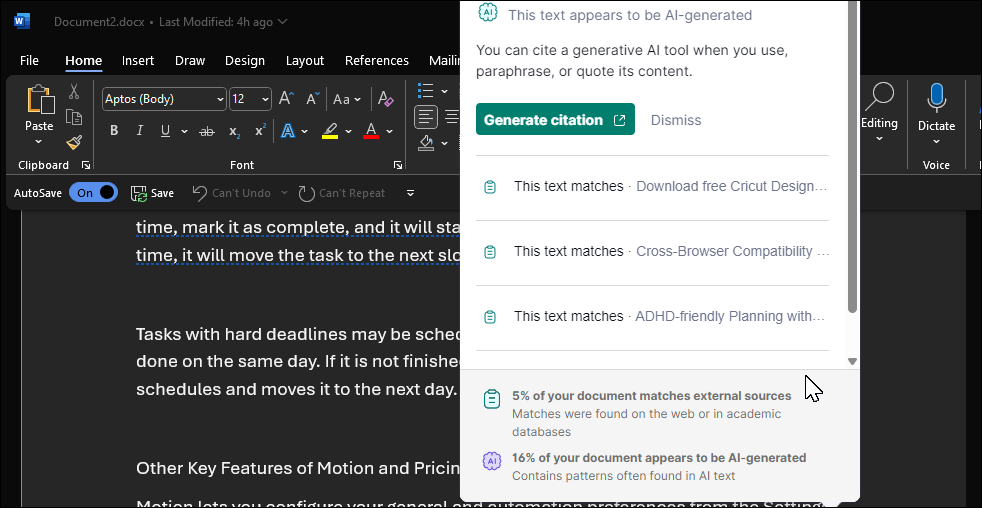
I tested the tool by copying texts from one of my published articles here at MakeUseOf. Microsoft Editor runs the text in your Word document against online resources using Bing, Microsoft’s search engine. When the check is complete, the Editor indicates the percentage of text found online. In this instance, it flagged 70% of the text content as seen online.
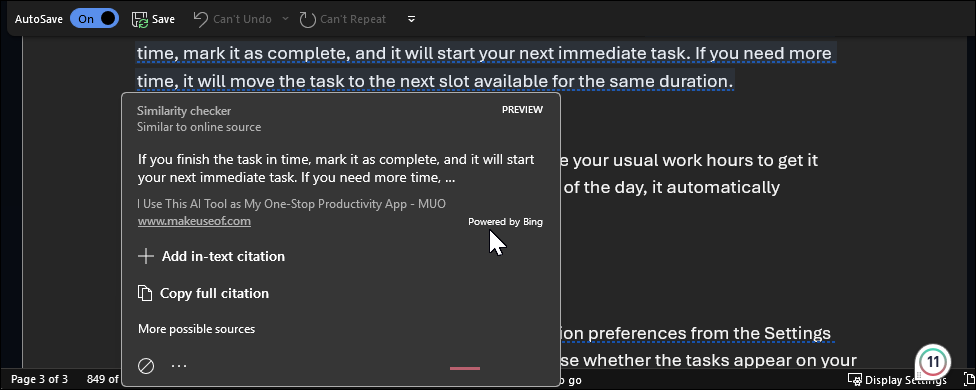
Additionally, you can click Similarities reviewed under the Similarities section to view the passages for potential plagiarism issues. By selecting a highlighted passage, you can either add a full citation or click the Next button (right arrow icon) to view the next passage and take the necessary action.
Is Microsoft Editor’s Plagiarism Checker Any Good?
For a quick comparison, I ran the same text through Grammarly’s plagiarism checker and noticed a stark difference between how these two tools work. While the Editor accurately identified the source of the text as MakeUseOf and flagged 70% of the content, Grammarly only detected 5% of the content as matching and also failed to cite the proper source.
This discrepancy is largely due to the way different plagiarism checkers work. While Microsoft Editor taps into Bing to detect similar content online, Grammarly relies on its own database of web pages and academic papers, which may not have indexed newer material yet. Also, Grammarly will likely perform better when checking plagiarism in an academic setup and for AI detection.
Despite its accuracy, Microsoft Editor seems to have a hard time detecting plagiarism in heavily modified text. That said, for Microsoft 365 subscribers, it’s a handy way to quickly review school work and other documents for copy-pasted work.
For those without a Microsoft 365 subscription, there are plenty of third-party plagiarism checkers that offer advanced detection for both plagiarized and AI-generated texts.